
Precisely, this study was to present and empirically validate a research model based on user behavior that examine m-government acceptance in developing countries and inspect the moderating role of facilitating conditions on m-government adoption. Therefore, this study aims at investigating the factors that influence individuals in adoption of new technology, specifically m-government in the context of developing countries. M-government has been singled out as one of the fundamental aspect for socio-economic growth in developing countries.

Technological development in the past decade has motivated governments in developing countries to focus on leveraging new technologies for efficient and effective public service delivery. The paper finally outlines research needs for a comprehensive design framework for m-government solutions and presents initial requirements for the framework. Design approaches are analysed by the Content, Context and Process (CCP) framework and are examined to identify requirements, methods and guidelines addressed. The challenges are categorised based on the factors of PESTELMO and are further examined to identify requirements for suitable m-government design. This paper aims to (1) identify challenges of m-government in developed and developing countries and (2) investigate approaches used for designing m-government applications. Design approaches in the literature lack a comprehensive way of addressing m-government challenges. However, research on the design of m-government applications is still scarce. Literature studies report on the significance of m-government, including its motivation, success, and failure in developed and developing countries. The ubiquity of mobile devices has drawn new attention to the field of electronic government. Also, its adoption reduces technological inconsistency of applications and service redundancy. The framework ensures that its users address all critical parties' and concerns related to the design of m-government services and to meeting user requirements. The target group of the framework is government organizations and designers responsible for designing mobile public services in developing countries. Subsequently, experts of ‘e’ and ‘m’-government and architects of information systems participated in the evaluation of the framework to assess its applicability and usefulness. The components comprise a method, viewpoints, a metamodel, stakeholder management, design principles, design guidelines, framework enablers, and a repository. The synthesis of literature and empirical findings were the main inputs to construct the components of the proposed framework.
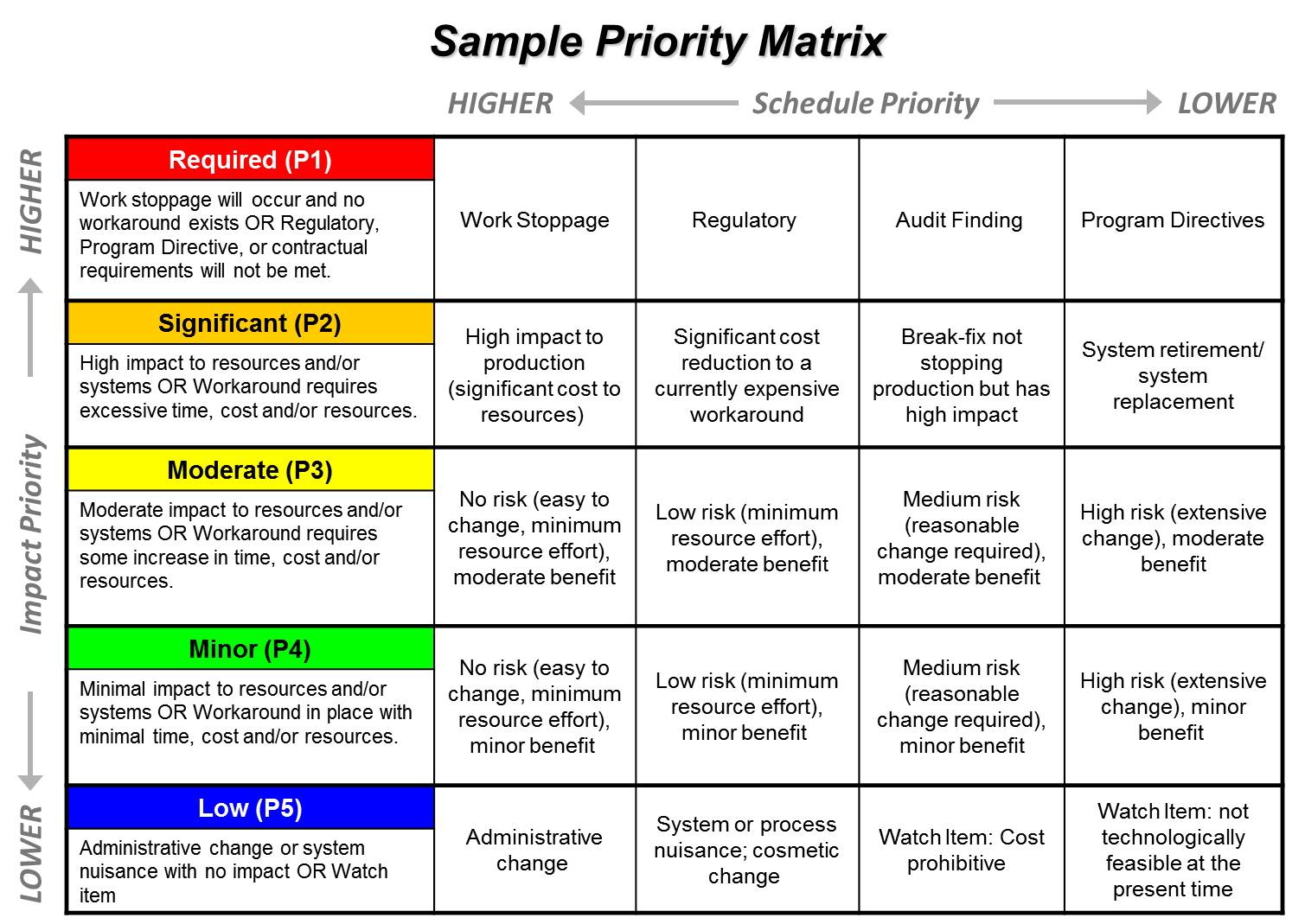
COMMUNICATION PRIORITY MATRIX SOFTWARE
MAXQDA software was used to analyze the collected raw data. Also, the thesis applied a follow-up interview to deepen the knowledge of results obtained from the online survey and to examine stakeholder management. The empirical research investigated the design approaches used, challenges faced and recommended activities and components for a proposed framework via an online questionnaire. This thesis aims to develop a comprehensive framework to bridge the gap in developing countries. Results unveiled a lack of research on designing such services while considering essential design activities systematically and comprehensively.
Also, the literature examined commercial mobile application development frameworks, enterprise architectures and agile methods to study their contribution to designing mobile public services. The former identified and analyzed the success factors, challenges, and design approaches for designing such services. The thesis applied design science research including literature review and empirical research to study the m-government context. Therefore, this thesis explored the design of mobile government applications and services by studying its status quo including current obstacles, requirements, and approaches deployed to design such services. The three recent UN global e-government surveys emphasize the adoption of mobile devices and cheap channels to address these challenges. The deployment of such tools for disseminating information in developing countries poses several challenges such as service inaccessibility and unavailability due to poor internet connectivity, the high price of devices, and poor service usability as a result of unskilled designers and illiterate users.
As a result, governments strive to offer their services electronically to citizens through electronic devices such as desktop and kiosk (also, known as electronic government or e-government). Using ICT to deliver community services supports SDGs such as equal access to information concerning community matters.

Global reports, discussions, and forums advocate the use of Information Communication Technologies (ICTs) in promoting sustainable development goals (SDGs ) published by the United Nations (UN).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
